

I’d still opt for a CMR drive – what kind of discount are we talking about, to be fair? 10% is not worth it in my opinion. I guess – thinking about selfhosting something like Plex or Nextcloud… or a DIY NAS. Those movies will not get edited, deleted or anything – they will just be read when you watch them. Like if you were to just fill it up with movies and that’s it. *5 = WD10EFRX, WD20EFZX, WD30EFZX, WD40EFZX, WD60EFZX, WD80EFBX, WD80EFZX, WD101EFBX, WD120EFBX, WD140EFGX When does buying a SMR drive make sense?īut if you get an amazing price, and you know that hard drive will not get a lot of writes, edits, and deletions… well, it might make sense since the actual heavy usage of erasing,editing and writing data is causing the ‘slowness’. It was last looked up in, on the manufacturers’ websites, just so you know. Please, search online or on the manufacturer’s website in case the below data becomes outdated. Here’s a breakdown of what is what usually, at least for the common models.
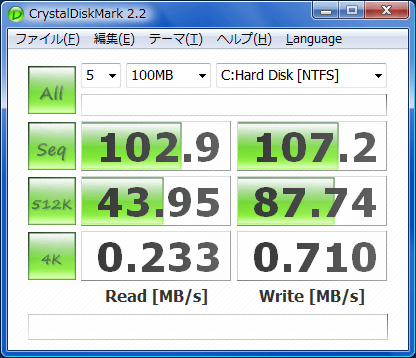
ST500LM030 CRYSTAL DISKMARK PDF
Neat!įor Seagate, however, you have to go to the product page, and download the PDF datasheet. Now, Western Digital, on their homepage in the shop section, actually lists CMR or SMR for their drives in the ‘Full Specifications’ area, at the Recording Technology specification.
ST500LM030 CRYSTAL DISKMARK CODE
But basically, searching with something like ‘product code SMR or CMR’ on Google will lead you to a good result most of the time. Some manufacturers make it easy, some not so much. How can I tell if the HDD I want to buy is SMR or CMR? This causes an impact on the overall read and write performance of the drive. If you hit the respective SMR drive hard with write and read operations, it won’t get to do this in a fast way, and the drive will have to write new data and reorganize stuff at the same time. This reorganization procedure must occur and makes idle time essential on an SMR drive. Then, when the SMR HDD becomes idle, it will enter a ‘reorganization mode’, where the old bits of data on the original track are being erased and made available for future use. While the original track with the old data will temporarily sit put. It will write the new data on an empty area of the disk.

Well, it depends on how you use the drive.īut! On an SMR drive, when any data is edited or overwritten, the write head will not overwrite data on the existing magnetic track. So we have a pretty good read speed, right? No matter what we choose? Right? Kind of. In short, because you want the best performance for your dollar.īut to get a little bit more technical, regardless of whether an HDD uses CMR or SMR when some new data is written on the drive, the tracks are fully readable without performance impact. CMR vs SMR drives – why does it actually matter? a great image explanation from Synology for SMR drivesīy overalapping the tracks, write heads become a lot thinner, and we get a bigger areal density.One way to think about it is by comparing it to the shingles on a roof. And this happens because rather than writing each magnetic track without overlapping, SMR overlaps each new track with part of the previous track. Shingled Magnetic Recording, or SMR, is an extension to PMR. a great image explanation from Synology for CMR / PMR drivesĪnd because the write head is usually quite large in comparison to the read head, HDD manufacturers aim to shrinking the size of the write head – or do it as much as possible.The magnetic tracks are written side-by-side without overlapping. The way CMR works is by aligning the poles of the magnetic elements, which represent bits of data perpendicularly to the surface of the disk. It is also known as PMR that comes from Perpendicular Magnetic Recording. CMR or PMR drives – how they workĬMR comes from Conventional Magnetic Recording. Tip: some great benchmarks for hard disk drives are: Crystal Disk Mark, ATTO Disk Benchmark, HD Tune, and even PCMark has some storage benchmarks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
